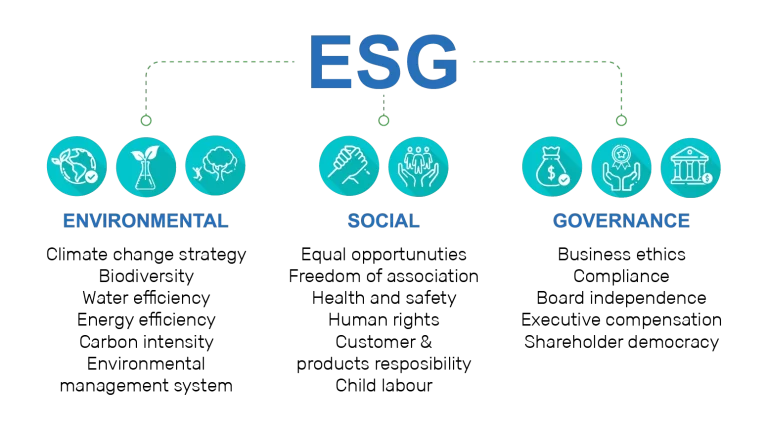
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance: The 3 central factors in measuring the sustainability and social impact of an investment in a company or business.
Environmental criteria include a company's impact on the environment, such as its carbon footprint, energy performance and use of renewable energy, waste management and recycling practices.
Social criteria include a company's treatment of its employees, customers and the communities it operates in.
Governance criteria include the policies, processes and practices that ensure the responsibility, transparency, and integrity within a company, setting the ground for sustainable business.
How to start creating an effective ESG strategy?
There is no standard method for defining crucial ESG factors for a company’s success and stakeholders’ priorities. A complete ESG approach includes due diligence, strategy, roadmap, KPIs, policies, analysis, and annual reviews.

Contact our experts and tell us about your project.
ESG is not just a trend, but a strategy for companies to benefit long-term business development, together with society and the environment.
ESG-focused companies create value for all stakeholders, and assume more responsibility and sustainability, leading to increased trust and loyalty from customers, employees and investors. These companies excel in risk management, spotting opportunities and making long-term sustainable decisions.
Strong ESG strategy is becoming a key factor in investment decisions, as more investors choose only ESG-compliant companies, recognizing the critical role that sustainable and socially responsible practices play in securing long-term value and positively impacting the world we live in.
In the ESG framework, climate change is considered an environmental issue, and companies are evaluated based on their efforts to mitigate climate-related risks and adapt to a low-carbon economy.
For sustainable building development, environmental concerns significantly affect portfolio risks and opportunities. Climate change is the number one risk and the foremost amplifying factor. It refers to the long-term shift in global weather patterns and temperatures primarily caused by human activities, particularly the emission of GHGs from burning fossil fuels and deforestation. Climate change poses significant risks to ecosystems, economies, and human well-being.
Carbon neutrality is a critical component in addressing climate change, as GHG emissions, such as carbon dioxide, have a significant role. New global legislations require companies and countries to neutralize their CO2 emissions by 2050.
The role of ESG in carbon neutrality is crucial. ESG considerations help companies to assess and understand their carbon footprint, identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to reduce emissions and achieve carbon neutrality.


The focus on ESG factors has grown as a result of increased awareness about the impact of corporate activities on the environment, society and the economy.
ESG investing began in the 1990s when people realized that looking at nonfinancial factors (like environmental impact and a company’s treatment of its employees) is necessary to predict a business’s success. Sustainability adepts started to identify several nonfinancial factors that should be included in the assessment of the long-term business development prospects.
The “triple bottom line” is the term embraced by the majority of sustainability consultants and refers to the financial, environmental and social factors to be included in calculating business performance. ESG can be viewed as a continuation and modernization of this concept, with the inclusion of the governance factor, which confirms that how a company is run will affect its long-term development.
As investors increasingly seek ESG-related information for investment purposes, many governments around the world have implemented regulations and disclosure requirements relating to ESG factors. International organizations such as the UN Principles for Responsible Investment have also been actively promoting and supporting these legal developments.